Artificial Intelligence (AI) automation is revolutionizing industries by streamlining processes, enhancing decision-making, and fostering innovation. This blog post delves into the multifaceted aspects of AI automation, exploring its benefits, challenges, and diverse applications across various sectors.
Key Findings
-
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: AI automation significantly reduces manual workload, allowing employees to focus on strategic tasks, thereby boosting overall productivity.
-
Cost Reduction: By automating routine processes, businesses can lower operational costs and minimize human errors.
-
Improved Decision-Making: AI systems analyze vast datasets to provide actionable insights, facilitating informed and timely decisions.
-
Scalability: AI automation enables organizations to scale operations efficiently without a proportional increase in resources.
-
Challenges: Implementing AI automation presents challenges such as data quality issues, integration complexities, and ethical considerations.
-
Industry Applications: AI automation is transforming sectors including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, retail, and marketing by optimizing processes and enhancing customer experiences.
Understanding AI Automation: Definition and Core Concepts
AI automation refers to the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies into automated systems, enabling them to perform tasks that traditionally require human intelligence. This fusion allows machines to learn from data, make decisions, and adapt to new situations with minimal human intervention.
Core Components of AI Automation
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): The simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, encompassing learning, reasoning, and self-correction.
-
Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data patterns and improve their performance over time without explicit programming.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Allows machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language, facilitating interactions such as chatbots and virtual assistants.
-
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Involves using software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
By combining these components, AI automation streamlines complex processes, reduces human error, and enhances decision-making capabilities across various industries.
External Sources: Learn More
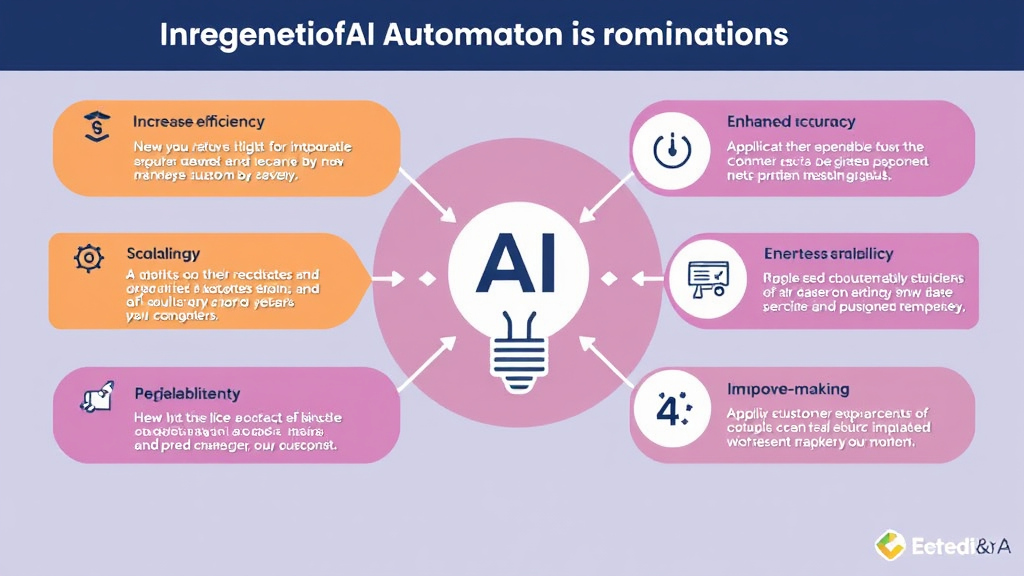
Key Benefits of Implementing AI Automation in Business Operations
Implementing AI automation in business operations offers several key benefits:
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
AI automates repetitive and time-consuming tasks, allowing employees to focus on strategic initiatives. For instance, in retail, AI-powered systems can track inventory in real time, reorder stock automatically, and predict future needs based on sales data, thereby optimizing stock levels and reducing manual workload.
Cost Savings
By automating routine tasks, businesses can reduce labor costs and operational inefficiencies. AI-driven systems operate continuously without breaks, leading to significant cost savings over time. For example, AI-powered manufacturing robots perform routine tasks on assembly lines faster and more accurately than humans, reducing labor costs and minimizing waste from defects.
Enhanced Accuracy
AI systems minimize errors and inconsistencies in business operations. With AI automation, businesses can achieve a higher degree of accuracy and precision in tasks such as data entry, inventory management, and quality control.
Scalability
AI-powered automation allows businesses to scale operations without proportionately increasing their workforce. AI systems can handle growing workloads without needing more employees, enabling businesses to expand operations while keeping costs low.
Improved Customer Experience
AI enhances customer experiences by providing personalized service and faster issue resolution. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants offer 24/7 support, answering customer queries in real time and anticipating customer needs to deliver customized solutions, resulting in higher satisfaction and a more seamless interaction.
Enhanced Decision-Making
AI tools analyze large datasets in real-time, providing businesses with actionable insights. Predictive analytics help companies make data-driven decisions, improve forecasting, and optimize strategies for maximum efficiency. AI also enhances decision-making by identifying trends and patterns that humans might overlook.
By integrating AI automation into business operations, organizations can achieve significant improvements in efficiency, cost savings, accuracy, scalability, customer satisfaction, and decision-making capabilities.
External Sources: Learn More
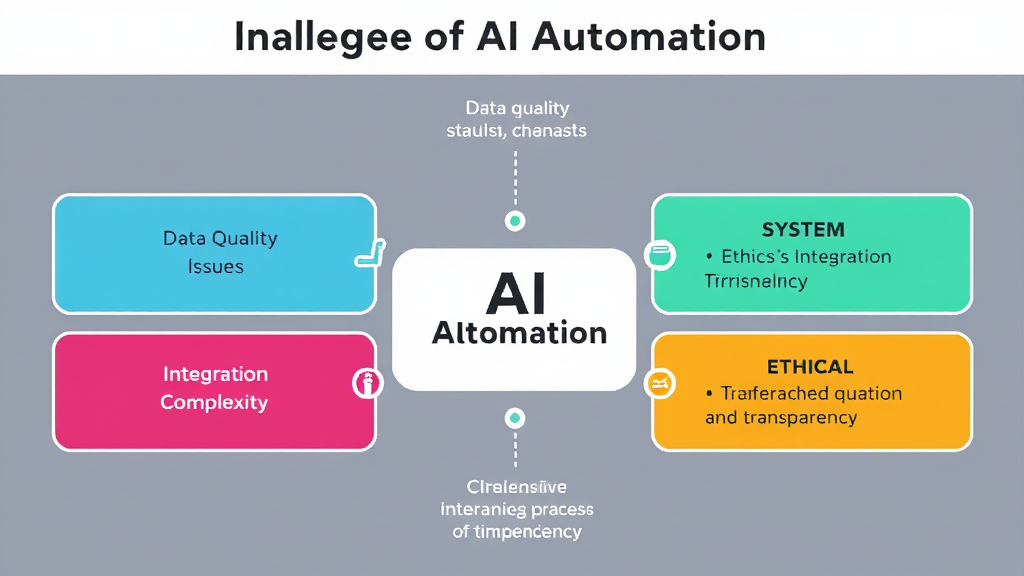
Overcoming Challenges in AI Automation: Data Quality, Integration, and Ethics
Implementing AI automation presents several challenges, notably in data quality, system integration, and ethical considerations. Addressing these issues is crucial for the successful deployment and operation of AI systems.
Data Quality
High-quality data is fundamental to the effectiveness of AI systems. Challenges in this area include:
-
Inaccurate Data: Errors from human input or faulty sensors can mislead AI models, leading to incorrect outcomes.
-
Outdated Data: Using stale information can result in decisions that don't reflect current realities.
-
Duplicate Data: Redundant records can skew analyses and introduce biases.
-
Inconsistent Data: Variations in data formats from multiple sources can complicate integration and analysis.
-
Biased Data: Non-representative datasets can cause AI systems to perpetuate existing biases.
To mitigate these issues, organizations should implement robust data governance practices, including regular audits and validation processes.
System Integration
Integrating AI into existing infrastructures poses several challenges:
-
Data Interoperability: Disparate data formats across systems can hinder seamless integration.
-
Training and Upskilling: Employees may require new skills to effectively collaborate with AI technologies.
-
System Compatibility: Legacy systems may not be optimized for AI, leading to compatibility issues.
A strategic integration plan, involving stakeholder collaboration and phased implementation, can help overcome these obstacles.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical challenges in AI automation include:
-
Bias and Fairness: AI systems can inherit biases from training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes.
-
Transparency and Explainability: Complex AI models may operate as "black boxes," making it difficult to understand their decision-making processes.
-
Privacy and Data Security: Handling large volumes of personal data raises concerns about misuse and breaches.
-
Accountability: Determining responsibility for AI-driven decisions can be complex.
To address these concerns, organizations should adopt ethical frameworks that promote fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI development and deployment.
By proactively tackling these challenges, organizations can harness the full potential of AI automation while ensuring responsible and ethical use.
External Sources: Learn More
Transform your workflow and unleash your potential—visit ipsom.io or drop us a line at office@ipsom.io.
AI Automation in Manufacturing: Enhancing Efficiency and Predictive Maintenance
AI automation is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry by enhancing operational efficiency and enabling predictive maintenance strategies. By integrating AI technologies, manufacturers can optimize production processes, reduce downtime, and extend equipment lifespan.
Enhancing Efficiency through AI Automation
AI-driven systems analyze vast amounts of data from manufacturing operations to identify patterns and optimize workflows. This leads to significant improvements in productivity and quality. For instance, companies like Siemens and GE have implemented AI for real-time defect detection and predictive maintenance, achieving higher efficiency and lower costs.
Predictive Maintenance: A Proactive Approach
Predictive maintenance leverages AI to monitor equipment health and predict potential failures before they occur. This proactive strategy offers several benefits:
-
Reduced Downtime: By anticipating equipment issues, manufacturers can schedule maintenance during non-peak hours, minimizing production disruptions.
-
Cost Savings: Preventing unexpected failures reduces repair costs and extends the lifespan of equipment.
-
Improved Safety: Anticipating equipment malfunctions enhances workplace safety by addressing potential hazards proactively.
-
Enhanced Efficiency: Maintenance teams can focus on critical tasks rather than routine inspections, improving overall operational efficiency.
-
Data-Driven Decision Making: AI provides valuable insights into equipment performance, aiding in strategic planning and continuous improvement initiatives.
By integrating AI automation and predictive maintenance, manufacturers can achieve a more efficient, cost-effective, and reliable production environment.
External Sources: Learn More
Transform your business with seamless automation—get started at ipsom.io or drop us a line at office@ipsom.io.
Transforming Healthcare with AI Automation: Diagnostics and Patient Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing diagnostic accuracy and streamlining patient management processes.
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
AI algorithms, particularly those based on deep learning, have demonstrated remarkable accuracy in diagnosing diseases from medical images and test results. These systems are trained on vast datasets, allowing them to recognize patterns and anomalies that might be imperceptible to the human eye. For example, in dermatology, AI systems trained on images of skin lesions have shown the ability to detect skin cancers, such as melanoma, with a level of precision comparable to that of experienced dermatologists.
Improved Patient Management
AI-powered tools provide personalized patient care by tailoring treatments based on individual health data. These tools continuously monitor patients' vitals, alerting healthcare providers to changes. This real-time monitoring ensures timely interventions and improves overall patient management, enhancing the quality of care.
By integrating AI into healthcare systems, medical professionals can deliver more accurate diagnoses and efficient patient care, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
External Sources: Learn More
Financial Services and AI Automation: Fraud Detection and Risk Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the financial services industry by enhancing fraud detection and risk management processes. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, natural language processing (NLP), and real-time data analysis, AI systems can identify and mitigate potential threats more efficiently than traditional methods.
AI in Fraud Detection
AI-driven fraud detection systems analyze vast amounts of transaction data to identify anomalies and suspicious activities. These systems utilize machine learning models to learn from historical data, enabling them to detect complex fraud schemes that may evade conventional rule-based systems.
Key components of AI-powered fraud detection include:
-
Behavioral Analysis: AI models establish a baseline of normal user behavior by analyzing patterns such as spending habits, login times, and transaction locations. Deviations from this baseline can trigger alerts for potential fraudulent activity.
-
Real-Time Monitoring: AI systems process transactions as they occur, allowing for immediate detection and response to suspicious activities. This real-time capability minimizes the window for fraudsters to exploit vulnerabilities.
-
Anomaly Detection: By identifying patterns and correlations within large datasets, AI can detect subtle anomalies indicative of fraud, even if the specific fraudulent behavior has not been previously encountered.
For instance, Mastercard's AI-powered Decision Intelligence solution assesses billions of transactions to detect fraud patterns with twice the accuracy of conventional methods, enhancing fraud prevention while minimizing false declines.
AI in Risk Management
In risk management, AI enhances decision-making by analyzing market trends, economic data, and historical patterns to predict potential risks. This predictive capability allows financial institutions to proactively manage risks and comply with regulatory requirements.
Applications of AI in risk management include:
-
Predictive Modeling: AI-based models assess the likelihood of risk events by analyzing factors such as economic changes, market volatility, and political events, enabling proactive risk mitigation strategies.
-
Compliance Automation: AI-driven Regulatory Technology (RegTech) solutions automate compliance processes like Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML), reducing manual workloads and ensuring adherence to evolving regulations.
-
Credit Scoring: AI models evaluate a wide range of data, including non-traditional data points like social behavior, to provide more accurate risk assessments for loan approvals.
For example, JPMorgan Chase's Contract Intelligence (COiN) platform utilizes NLP and machine learning to analyze thousands of legal contracts within seconds, identifying risk factors and compliance gaps, thereby improving efficiency and accuracy in risk management.
While AI offers significant advantages in fraud detection and risk management, challenges such as data privacy concerns, algorithmic bias, and regulatory compliance must be addressed. Financial institutions are encouraged to implement AI solutions with robust governance frameworks and human oversight to ensure ethical and effective use.
External Sources: Learn More
Retail and Marketing: Personalization and Customer Engagement through AI Automation
AI automation is revolutionizing the retail and marketing sectors by enabling unprecedented levels of personalization and customer engagement. By analyzing vast amounts of customer data, AI systems can deliver tailored experiences that enhance satisfaction and drive sales.
Personalized Product Recommendations
Retailers like Amazon utilize AI algorithms to analyze customer behavior, including browsing history and purchase patterns, to suggest products that align with individual preferences. This approach has been highly effective, with personalized recommendations accounting for approximately 35% of Amazon's total revenue.
AI-Powered Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants have transformed customer service by providing instant, personalized responses to inquiries. For instance, Sephora's chatbot on Facebook Messenger assists customers in finding products, offers beauty tips, and schedules in-store appointments, significantly improving customer engagement and satisfaction.
Predictive Analytics for Customer Needs
AI's predictive analytics capabilities allow retailers to anticipate customer behaviors by analyzing historical data. This enables businesses to proactively address customer requirements, such as restocking popular products or offering timely promotions, thereby enhancing customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Dynamic Pricing Strategies
AI enables dynamic pricing by analyzing market trends, customer behavior, and competitor pricing to adjust product prices in real-time. This approach ensures that customers receive value while helping retailers remain competitive without eroding their margins.
Ethical Considerations
While AI offers numerous benefits, it also raises ethical concerns, particularly regarding consumer privacy and fairness. A study highlighted that many consumers are concerned about the amount of personal data collected by AI-driven retail applications and the potential for algorithmic bias. Retailers must prioritize transparency, fairness, and data protection when deploying AI systems to maintain consumer trust.
By leveraging AI automation, retailers and marketers can create more personalized and engaging customer experiences, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty. However, it is crucial to address ethical considerations to ensure the responsible use of AI technologies.
External Sources: Learn More
Transform your workflow and elevate your business—get started with ipsom.io or connect with us at office@ipsom.io!
The Future of Work: AI Automation's Impact on Employment and Skill Development
Artificial Intelligence (AI) automation is profoundly transforming the employment landscape, introducing both challenges and opportunities.
Job Displacement and Creation:
AI's integration into various sectors has led to the automation of routine tasks, resulting in the displacement of certain roles, particularly in entry-level white-collar positions. Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei predicts that AI could eliminate up to 50% of these roles within the next five years. However, this technological shift also fosters the creation of new, specialized positions that require advanced technical skills, such as data analysis and machine learning. This dual effect underscores the need for a workforce that is adaptable and equipped with relevant competencies.
Skill Development and Lifelong Learning:
The rapid adoption of AI accentuates existing skill gaps, particularly among workers in roles susceptible to automation. To remain competitive, employees must acquire new skills, including digital literacy and data science. Governments, educational institutions, and businesses are collaborating to provide training programs and reskilling opportunities, aiming to bridge these gaps and promote economic mobility.
Impact on Job Quality:
AI has the potential to enhance job quality by automating tedious, repetitive tasks, allowing workers to focus on more complex and rewarding activities. For instance, in the financial sector, AI systems have reduced simple administrative tasks, enabling employees to spend more time supporting customers and colleagues, thereby increasing job satisfaction.
Addressing Inequality:
While AI-driven automation can lead to job displacement, it also creates opportunities for new, high-skilled positions. However, these roles often require advanced education and training, which may not be accessible to all workers, potentially widening income inequality. To mitigate this, it is crucial to invest in education and training programs that equip workers with the necessary skills to thrive in an AI-driven economy.
In summary, AI automation is reshaping employment and skill development, necessitating proactive strategies to address challenges and leverage opportunities. Emphasizing lifelong learning, reskilling initiatives, and policies that promote inclusivity will be essential in navigating this evolving landscape.
External Sources: Learn More
Transform your workflow and embrace automation—visit ipsom.io or email us at office@ipsom.io.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
What is AI automation and how does it differ from traditional automation?
AI automation refers to systems that utilize artificial intelligence to perform tasks traditionally requiring human intelligence, such as learning from data, making decisions, and adapting to new information. Unlike traditional automation, which follows predefined rules and handles repetitive, rule-based tasks, AI automation can process unstructured data, recognize patterns, and make informed decisions autonomously. This adaptability allows AI automation to manage complex and dynamic tasks, whereas traditional automation is limited to static, predictable processes.
What are the primary benefits of integrating AI automation into business processes?
Integrating AI automation into business processes offers several key benefits:
-
Increased Efficiency and Productivity: AI automates repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on strategic initiatives, thereby boosting overall productivity.
-
Cost Savings: By reducing labor costs and operational inefficiencies, AI-driven systems work continuously without breaks, leading to significant financial savings.
-
Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors: AI systems minimize costly errors, ensuring high accuracy and consistency in data-heavy tasks such as analysis and financial forecasting.
-
Improved Decision-Making: AI analyzes large datasets in real-time, providing actionable insights that enhance decision-making and strategic planning.
-
Scalability: AI-powered automation easily scales to handle growing workloads without a corresponding increase in costs or effort, adapting to business growth seamlessly.
-
Enhanced Customer Experience: AI enhances customer experiences by providing personalized service and faster issue resolution through tools like chatbots and virtual assistants.
-
Data-Driven Insights: AI automation generates vast amounts of data, which can be analyzed to extract valuable insights, driving innovation and maintaining a competitive edge.
These advantages collectively contribute to streamlined operations, improved efficiency, and sustained business growth.
What challenges do organizations face when implementing AI automation?
Organizations face several challenges when implementing AI automation:
-
Data Quality and Availability: AI systems require large volumes of accurate and well-organized data. Many organizations struggle with disorganized or incomplete data, leading to poor model performance.
-
Integration with Existing Systems: Incorporating AI into legacy systems can be complex and costly, often requiring significant re-engineering to ensure compatibility and seamless operation.
-
High Implementation Costs: The initial investment for AI tools, infrastructure, and specialized talent can be substantial, posing a barrier, especially for smaller businesses.
-
Skills Gap and Talent Shortages: There's a limited pool of AI professionals, making it challenging to find and retain the necessary expertise for development and maintenance.
-
Employee Resistance to Change: Employees may fear job displacement or struggle to adapt to new technologies, leading to reluctance in adopting AI solutions.
-
Ethical and Regulatory Concerns: Ensuring AI systems operate ethically and comply with regulations is crucial, as issues like algorithmic bias and data privacy can pose significant risks.
-
Lack of Leadership Support: Without active involvement from leadership, AI initiatives may lack direction and fail to align with organizational goals.
-
Insufficient IT Infrastructure: Outdated systems may lack the processing capabilities required for AI, necessitating significant upgrades or replacements.
-
Data Privacy and Security Concerns: Handling sensitive information with AI systems raises risks, making compliance with data protection regulations essential.
-
Organizational Silos: Limited cross-functional collaboration can hinder AI projects that span multiple departments, emphasizing the need for a culture of collaboration.
Addressing these challenges requires strategic planning, investment in infrastructure and talent, effective change management, and adherence to ethical standards.
How is AI automation transforming the manufacturing industry?
AI automation is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry by enhancing efficiency, quality, and adaptability. Key transformations include:
-
Predictive Maintenance: AI analyzes equipment data to predict failures, enabling proactive maintenance that reduces downtime and extends machinery lifespan.
-
Quality Control: AI-powered systems utilize computer vision to detect defects in real-time, ensuring consistent product quality and minimizing waste.
-
Supply Chain Optimization: AI enhances demand forecasting and inventory management, leading to more efficient supply chains and reduced operational costs.
-
Process Optimization: AI identifies bottlenecks and inefficiencies in production processes, recommending improvements to streamline operations and boost productivity.
-
Workforce Transformation: While AI automates repetitive tasks, it also creates new roles requiring advanced technical skills, prompting a shift in workforce dynamics.
These advancements position AI as a pivotal force in modernizing manufacturing, driving innovation and competitiveness.
In what ways does AI automation enhance customer experiences in retail?
AI automation enhances customer experiences in retail through several key avenues:
-
Personalized Shopping Experiences: AI analyzes customer data, such as past purchases and browsing history, to offer tailored product recommendations, increasing engagement and satisfaction.
-
24/7 Customer Support: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide instant, round-the-clock responses to customer inquiries, handling routine questions and allowing human agents to focus on complex issues.
-
Efficient Inventory Management: AI predicts demand by analyzing historical sales data and market trends, helping retailers optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and minimize overstock situations.
-
Enhanced In-Store Experiences: AI enables virtual try-ons and augmented reality applications, allowing customers to visualize products before purchasing, thereby boosting confidence and reducing returns.
-
Improved Customer Insights: AI analyzes customer feedback from various channels to gauge sentiment, identify areas for improvement, and proactively address issues, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Streamlined Operations: AI automates routine tasks like data entry and email management, freeing human agents to focus on more complex and value-added activities, thus enhancing overall efficiency.
By integrating AI automation, retailers can deliver more personalized, efficient, and engaging customer experiences.
What impact does AI automation have on employment and workforce skills?
AI automation is transforming employment and workforce skills in several key ways:
Job Displacement and Creation: AI is automating routine tasks, leading to the displacement of certain roles, particularly in entry-level white-collar jobs. Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei predicts that AI could eliminate up to 50% of these positions within five years. However, AI also creates new job categories, especially in technology-driven fields, necessitating a shift in workforce skills.
Skill Shifts and Reskilling: The demand for technical skills such as data analysis, programming, and machine learning is increasing. Soft skills like creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence are also becoming more valuable, as they are less susceptible to automation. This shift underscores the importance of reskilling and upskilling programs to help workers adapt to new roles.
Wage Inequality: AI-driven automation can lead to wage suppression for low-skilled labor due to decreased demand, while increasing wages for high-skilled tech professionals, thereby widening income disparities.
Ethical Considerations: The integration of AI into workforce management raises ethical issues, including potential biases in AI algorithms and concerns about job displacement. Addressing these challenges requires proactive measures to ensure fairness and transparency in AI deployment.
In summary, AI automation is reshaping the employment landscape by displacing certain jobs, creating new opportunities, and altering the skills required in the workforce. Proactive reskilling and upskilling initiatives are essential to equip workers for these changes.
How can businesses ensure ethical use of AI automation?
To ensure the ethical use of AI automation, businesses should:
-
Develop Ethical AI Policies: Establish clear guidelines that align with company values and address issues like bias, transparency, and accountability.
-
Form Oversight Committees: Create dedicated teams to monitor AI deployment, assess risks, and ensure compliance with ethical standards.
-
Conduct Regular Audits: Periodically review AI systems to identify and mitigate biases, ensuring fairness and reliability.
-
Ensure Transparency: Clearly communicate how AI systems make decisions and inform stakeholders about AI usage.
-
Prioritize Data Privacy: Implement robust data protection measures and comply with relevant regulations to safeguard user information.
-
Provide Employee Training: Educate staff on AI ethics, potential biases, and responsible usage to foster an ethical culture.
-
Engage Stakeholders: Involve diverse groups in AI development to consider multiple perspectives and promote inclusivity.
-
Maintain Human Oversight: Ensure human intervention in critical AI decisions to uphold accountability and address ethical concerns.
By implementing these practices, businesses can responsibly integrate AI automation while upholding ethical standards.
What are some real-world examples of successful AI automation implementations?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been successfully implemented across various industries, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Here are some notable examples:
Manufacturing:
-
Tesla's Robotic Assembly Line: Tesla employs AI-powered robotic arms to handle tasks such as welding, painting, and component assembly. This integration has increased production speed by approximately 25% and reduced defects by 20%, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
-
Siemens' Predictive Maintenance: Siemens utilizes AI to analyze real-time sensor data from industrial equipment, predicting failures before they occur. This proactive approach has reduced unplanned downtime by 25%.
Retail:
-
Amazon's Fulfillment Centers: Amazon's fulfillment centers are powered by AI-enabled robots that manage inventory and process orders. This automation has increased order fulfillment speed by 40% and improved space utilization by 50%.
-
Walmart's Inventory Management: Walmart integrates AI into its inventory management and customer experience strategies, optimizing its supply chain and reducing waste. AI-powered demand forecasting has led to a significant reduction in overstocking and understocking, saving the company millions of dollars annually.
Healthcare:
-
Mayo Clinic's AI-Powered Diagnostics: Mayo Clinic integrates AI into its diagnostic processes to enhance the accuracy and speed of patient assessments. This has led to a 30% improvement in early cancer detection and a significant reduction in misdiagnoses.
-
Google's Medical Diagnostics: Google partnered with Moorfields Eye Hospital to develop AI that analyzes 3D eye scans, achieving 94% accuracy in detecting over 50 eye diseases.
Finance:
-
JPMorgan Chase's Algorithmic Trading: JPMorgan Chase developed "LOXM," an AI tool that executes high-frequency trades autonomously, adapting to market volatility faster than human traders.
-
Mastercard's AI-Based Fraud Detection: Mastercard employs AI to monitor transactions and flag unusual behavior in real-time, reducing false declines by 50% and enhancing overall transaction security.
Transportation:
-
Tesla's Autonomous Driving: Tesla integrates AI and machine learning into their vehicles to enable autonomous driving features. This has improved vehicle safety and increased customer satisfaction.
-
Waymo's Self-Driving Cars: Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., has developed AI-powered self-driving cars that aim to reduce accidents and improve traffic efficiency.
Energy:
- DeepMind's Data Center Cooling: DeepMind, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., used AI to improve the energy efficiency of Google's data centers, reducing energy consumption by up to 40%.
These examples demonstrate the transformative impact of AI automation across diverse sectors, leading to enhanced operational efficiency, cost savings, and improved customer experiences.
How does AI automation contribute to cost savings in organizations?
AI automation contributes to cost savings in organizations through several key mechanisms:
-
Labor Cost Reduction: By automating repetitive tasks such as data entry, customer inquiries, and payroll processing, AI reduces the need for manual labor. This shift allows employees to focus on higher-value activities, leading to significant labor cost savings.
-
Operational Efficiency: AI enhances productivity by streamlining workflows and optimizing resource allocation. For instance, predictive maintenance powered by AI can reduce equipment downtime by up to 50%, thereby lowering maintenance costs and improving overall efficiency.
-
Error Reduction: Automated systems minimize human errors in processes like data processing and invoicing, leading to fewer costly mistakes and rework. This accuracy not only saves money but also improves service quality.
-
Energy Management: AI algorithms can optimize energy consumption by predicting demand and adjusting usage accordingly, resulting in significant cost savings.
-
Compliance and Risk Management: AI systems offer continuous monitoring of compliance-related activities, identifying potential risks as they emerge. This proactive approach prevents non-compliance issues from escalating, thereby reducing the overall cost of compliance.
-
Supply Chain Optimization: AI enhances supply chain efficiency by optimizing inventory levels, predicting demand fluctuations, and managing logistics more effectively. This leads to reduced warehousing costs and improved supply chain resilience.
By implementing AI automation in these areas, organizations can achieve substantial cost savings and enhance their competitive edge.
What future trends are expected in the field of AI automation?
The field of AI automation is poised for significant advancements in the coming years. Key trends include:
1. Agentic AI
Agentic AI refers to autonomous systems capable of making decisions and performing tasks without human intervention. These systems utilize techniques like natural language processing, machine learning, and computer vision to adapt and optimize processes dynamically.
2. Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation involves integrating multiple automation technologies, such as AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA), to create comprehensive end-to-end automation solutions. This approach aims to streamline operations and enhance efficiency across various business processes.
3. Human-Centered AI
Human-centered AI focuses on developing systems that prioritize human values and needs, aiming to augment human intelligence rather than replace it. This approach emphasizes ethical considerations and the enhancement of human capabilities through AI collaboration.
4. AI and Cloud Integration
The integration of AI with cloud computing is set to revolutionize data processing and storage. This trend will enable businesses to leverage AI capabilities without the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure, making AI more accessible and scalable.
5. AI in Edge Computing
Edge computing involves processing data closer to where it is generated, reducing latency and improving speed for critical applications. AI is increasingly being integrated into edge computing, enabling faster, more efficient data processing in industries such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and smart cities.
6. AI-Driven Personalization
AI is driving a trend towards hyper-personalization in customer experiences. By analyzing customer data and predicting preferences, AI can deliver personalized recommendations and tailored content, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
7. AI in Cybersecurity
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, AI will play a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity measures. AI-driven security systems will be able to detect and respond to threats in real-time, providing a higher level of protection for businesses and individuals.
8. AI in Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry will continue to benefit from AI automation. AI-driven robots and systems will improve production efficiency, reduce errors, and lower costs, leading to more innovative and competitive manufacturing processes.
9. AI in Customer Service
AI-powered customer service solutions, such as chatbots and virtual assistants, will become even more prevalent. These tools will provide more personalized and efficient customer interactions, improving customer satisfaction and reducing operational costs.
10. AI in Decision-Making
Businesses are increasingly using AI to support decision-making processes. From strategic planning to real-time operational decisions, AI can analyze vast amounts of data and provide insights that help businesses make better, more informed choices.
These trends indicate a future where AI automation becomes more integrated, intelligent, and aligned with human values, driving efficiency and innovation across various industries.